4.7bn diagnostic imaging procedures were performed globally in 2021, representing a strong recovery over 2020. Healthy demand for teleradiology services resulted in the global penetration of teleradiology reads into diagnostic imaging procedures bouncing back to 1.9%, and the overall teleradiology reading services and IT market revenue elevating past its pre-pandemic level to USD $1.7bn. With a projection for the market to reach USD $3.7bn in 2026, here I explore five drivers fueling this period of robust growth.
1. Radiologist shortage leading to improved compensation
The accelerated post-pandemic demand for teleradiology services has posed a new set of challenges for vendors, such as ensuring adequate resourcing capacity. This is a task made tougher by an unprecedented radiologist shortage, particularly in the US, driven by burnout and wage inflation. This has caused considerably longer turnaround times for non-urgent diagnostic examinations. To attract and retain radiologists, teleradiology market leader vRad set the tone 12 months ago, announcing a substantial radiologist compensation increase of up to 25%, beginning in January 2022. Staff increases ranging from between 10-30% have also been common across many US-based teleradiology providers this year.
Teleradiologist wage inflation and subsequent higher teleradiology reading service fees (+12% y-o-y global revenue per read projection in 2022) could be viewed as a barrier and deter some healthcare providers from outsourcing their diagnostic imaging workload. However, the reality is that most healthcare providers are in desperate need for external support and view teleradiology as a necessity to ensure efficient reading turnaround times and provide high-quality patient care. In addition, more than 50% of radiologists are over the age of 55, meaning that many experienced radiologists will be entering retirement over the next decade. With radiology demand (reading hours) rising at a faster pace than the supply of experienced radiologists, the shortfall between supply and demand is set to accelerate further.
2. Increased diagnostic procedures being performed
Prior to COVID-19, the volume of diagnostic imaging examinations had been growing annually by >3% and hit 5.0bn in 2019. Although volumes dipped in 2020, the strong recovery witnessed in 2021 is set to continue with volumes reaching >6bn by 2026. The number of examinations is being fueled by several well-known factors, including an aging population, rising demand for early disease diagnosis among patients and physicians, improved government funding towards chronic disorders, and increases in disposable income/middle-class populations, particularly in less developed geographies.
3. Rising demand for specialist imaging procedures
The utilization of CT and MRI is forecast to grow from a 21% share of overall US diagnostic imaging procedures in 2021 to 23% in 2026. In absolute terms, this translates to volume growth of 6% (CAGR), significantly outpacing the growth of other modalities, especially X-ray (+2% CAGR). As demand for specialized modalities increases, so does the requirement for specialist radiologists capable of interpreting more complex examinations. Where access to sub-specialty expertise can be limited in-house (e.g. in smaller hospitals), teleradiologist expertise provides an ideal solution.
4. Increased healthcare provider focus on operational efficiency, partly owing to reimbursement cuts
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) announcement (December 2020) to drastically cut diagnostic radiology reimbursement by 10% in 2021, and proposed 2022/2023 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) changes will impact the diagnostic imaging market. To some extent, reduced reimbursement rates may act as a market barrier and reduce the attractiveness of setting up a teleradiology reading service. However, reimbursement cuts are expected to place further pressure on US healthcare providers to reduce costs (e.g. downsize their internal workforce) and push to more outsourcing from hospitals, with an increased focus on operational efficiency; this is expected to drive additional demand for imaging IT/AI products and tools that enrich a provider or radiologist’s efficiency and productivity, whether that is increasing patient throughput or faster reading and reporting via teleradiology services.
5. AI Developments
Three of the most important factors that heavily influence the success of teleradiology reading service providers are the speed that teleradiologists perform and report on their reads; the accuracy of the reports produced by teleradiologists; and the workflow and decision support processes that service providers put in place to ensure urgent reads are prioritized and reported on quickly. Over time, AI can be used to support and improve all key ingredients for a successful teleradiology service.
Although AI usage in teleradiology image/clinical analysis remains relatively limited, most instances of AI adoption to-date have been in relation to improving teleradiology workflow efficiency. In the short-to-medium term, AI workflow optimization is expected to move towards wider teleradiology market adoption and support improvements in turnaround times.
Outlook for 2022 and Beyond
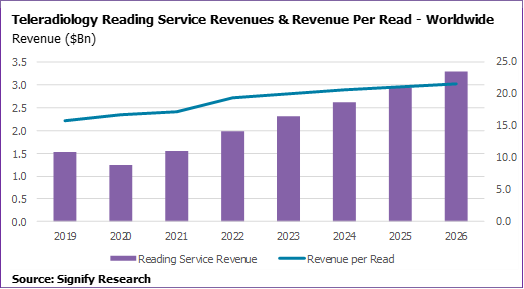
As displayed in the figure below, these market drivers are projected to result in teleradiology reading service revenues increasing by 30% in 2022 and 16% per annum (CAGR 2021-2026). Teleradiology reading volumes are on course for slightly lower double-digit growth over this period.
About Arun Gill, Senior Analyst at Signify Research
Arun Gil is a Senior Market Analyst at Signify Research, a UK-based market research firm focusing on health IT, digital health, and medical imaging. Arun joined Signify Research in 2019 as part of the Digital Health team focusing on EHR/EMR, integrated care technology, and telehealth. He brings with him 10 years of experience as a Senior Market Analyst covering the consumer tech and imaging industry with Futuresource Consulting and NetGrowth Consultants.
